LEXICAL DATABASE

|
Web dictionary demo represents an attempt to visualize Slovene Lexical Database on the web. You can also download the database. |
WHAT IS SLOVENE LEXICAL DATABASE?
SLOVENE LEXICAL DATABASE IN NUMBERS
The database contains 2,500 entries with 10,946 lexical units: senses, sub-senses, multi-word units and phraseological units.
| database entries | 2,500 | lexical units | 10,946 | collocations | 44,626 | ||
| nouns | 1,288 | senses | 4,371 | extended collocations | 4,602 | ||
| verbs | 528 | sub-senses | 3,076 | syntactic combinations | 8,298 | ||
| adjectives | 546 | multi-word units | 2,053 | syntactic patterns | 7,151 | ||
| adverbs | 138 | phrasological units | 1,446 | examples | 152,996 | ||
| labels | 1,197 | ||||||
| grammatical restrictions | 716 |
THE CONCEPT OF THE DATABASE AND ITS CONTENT
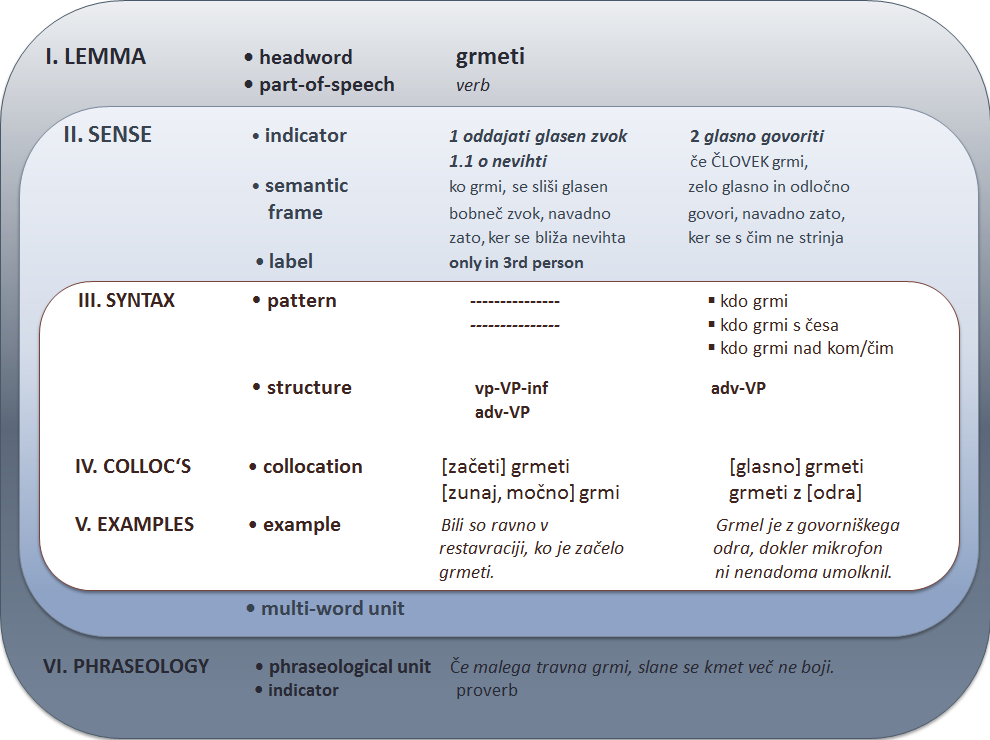
The database is structured as a network of interrelated semantic and syntactic information about a particular word. Semantic level represents the top level in the hierarchy with the lexical unit as its core element. This includes all senses of the headwrd, multi-word expressions and phraseological units. Each sense is described with a short semantic indicator and/or whole-sentence definition which includes typical syntactic environment of the headword with the relevant number, form and semantic types in a valency frame (semantic frame). These are also reflected in a number of syntactic structures and corresponding collocations. All the higher types of information are confirmed by a selection of corpus examples.
Multi-word expressions and phraseological units are treated independently from particular senses of the headword and have their own internal structure which requires the same types of information as single-word entries or senses.
WHO ARE THE USERS OF THE LEXICAL DATABASE?
In Slovene Lexical Database, data are organized in a modular manner and can be combined in different ways. They are accessible on different levels of abstraction taking into account also different possible end users.
General and school users will benefit from semantic descriptions in the form of short semantic indicators generating a sense menu for easier navigation through polysemic entry, as well as semantic frames containing whole-sentence definitions.
Collocations and corpus examples show how words are used in their most typical environment in real texts. They represent a direct and unmediated type of information on the word environment which is important for learning Slovene as a foreign language.
Linguists will be able to recognize basic valency patterns in whole-sentence definition and their relation with different possible syntactic realization which are frequently used in written communication by speakers of Slovene.
Encoded syntactic structures and patterns for each registered sense and subsense of the word are designed for language technologies to enable the improvement of automatic annotation of Slovene texts on the level of morpho-syntactic, syntactic and semantic levels, as well as to contribute to the development of language technology applications for Slovene in general.
AUTHORS AND COLLABORATORS
Technical support: Rok Rejc, Polonca Kocjančič
Administrative support: Karmen Kosem
BIBLIOGRAPHY
Guidelines
GANTAR, Polona, GRABNAR, Katja, KOCJANČIČ, Polona, KREK, Simon, POBIRK, Olga, REJC, Rok, ŠORLI, Mojca, ŠUSTER, Simon, ZARANŠEK, Petra, 2009: Specifikacije za izdelavo leksikalne baze za slovenščino: standard za izdelavo posamezne leksikalne enote v leksikalni bazi. Projekt »Sporazumevanje v slovenskem jeziku« ESS in MŠŠ.
GANTAR, Polona, GRABNAR, Katja, KOCJANČIČ, Polona, KREK, Simon, POBIRK, Olga, REJC, Rok, ŠORLI, Mojca, ŠUSTER, Simon, ZARANŠEK, Petra, 2009: Specifikacije za izdelavo leksikalne baze za slovenščino: opis analize referenčnega korpusa. Projekt »Sporazumevanje v slovenskem jeziku« ESS in MŠŠ.
Articles
FIŠER, Darja, GANTAR, Polona, KREK, Simon, 2012: Using explicitly and implicitly encoded semantic relations to map Slovene wordnet and Slovene lexical database. V: 8th International Conference on Language Resources and Evaluation, 21-27 May 2012, Istanbul, Turkey. LREC 2012 : proceedings (Workshops: Semantic relations II). Istanbul: ELRA, 2012. Str. 77-84.
GANTAR, Polona, 2011: Leksikalna baza za slovenščino: komu, zakaj in kako (naprej)?. Jezikoslovni zapiski, 2011, 17, št. 2. Str. 77-92.
GANTAR, Polona, 2010: K uporabniku usmerjeni slovnično-leksikalni opisi slovenskega jezika. V: GORJANC, Vojko (ur.), ŽELE, Andreja (ur.). Izzivi sodobnega jezikoslovja, (Zbirka Razprave FF). Ljubljana: Znanstvena založba Filozofske fakultete, 2010 Str. 35-51.
GANTAR, Polona, 2009: Leksikalna baza: vse, kar ste vedno želeli vedeti o jeziku. Jezik in slovstvo, letn. 54, št. ¾. Str. 69-94.
GANTAR, Polona, KREK, Simon, 2011: Slovene lexical database. V: Majchraková, D., Garabík, R. (ur.). Natural language processing, multilinguality: sixth international conference, Modra, Slovaška, 20-21. Oktober 2011. Str. 72-80.
GANTAR, Polona, KREK, Simon, 2009: Drugačen pogled na slovarske definicije: opisati, pojasniti, razložiti?. V: STABEJ, Marko (ur.). Infrastruktura slovenščine in slovenistike, Obdobja, Simpozij, = Symposium, 28). Ljubljana: Znanstvena založba Filozofske fakultete. Str. 151-159.
GRABNAR, Katja, 2010: Slikar slika, slikarka ilustrira? Vprašanje ženskih poimenovanj oseb v opisu sodobne slovenščine. V: VINTAR, Špela (ur.). Slovenske korpusne raziskave, (Zbirka Prevodoslovje in uporabno jezikoslovje). Ljubljana: Znanstvena založba Filozofske fakultete. Str.
KOCJANČIČ, Polonca, ZARANŠEK, Petra, 2009: The Slovene Lexical Database: The Organizing Principles of the Argument Structure. V: Sánchez Pérez, A., P. Cantos Gómez: A survey on corpus-based research [Elektronski vir] = Panorama de investigaciones basadas en corpus. Murcia: AELINCO. Str. 293-206.
KOSEM, Iztok, GANTAR, Polona, KREK, Simon, 2012: Avtomatično luščenje leksikalnih podatkov iz korpusa. V: T. Erjavec, J. Gros (ur.) Zbornik konference Jezikovne tehnologije. Institut Jožef Stefan, 8.-9.oktober 2012, Ljubljana.
KOSEM, Iztok, HUSÁK, Miloš, MCCARTHY, Diana, 2011: GDEX for Slovene. V: Kosem, I., Kosem K. (ur.): Electronic Lexicography in the 21st Century: New applications for new users. Proceedings of eLex 2011, Bled, 10-12 November 2011. Ljubljana: Trojina, zavod za uporabno slovenistiko. Str. 151-159.
KREK, Simon, 2012: New Slovene sketch grammar for automatic extraction of lexical data. SKEW3, tretja mednarodna delavnica orodja Sketch Engine, Brno, Češka, 21-22. marec 2012.
ŠORLI, Mojca, 2011: Pragmatic Components in the Slovene Lexical Database Descriptions. V: Kosem, I., Kosem K. (ur.): Electronic lexicography in the 21st century: new applications for new users. Proceedings of eLex 2011, 10-12 November 2011, Bled, Slovenia. Ljubljana: Trojina, Institute for Applied Slovene Studies. Str. 251-259.
ŠORLI, Mojca, 2010: The retrieval of data for Slovene-X dictionaries. V: Proceedings of the XIV Euralex International Congress. Leeuwarden, 6-10 July 2010. Ljouwert: Fryske Akademy. Str. 849-854.
ŠORLI, Mojca, 2009: Pridobivanje podatkov o slovenščini za izdelavo slovensko-tujejezičnih slovarjev. V: STABEJ, Marko (ur.). Infrastruktura slovenščine in slovenistike, Obdobja, Simpozij, = Symposium, 28. Ljubljana: Znanstvena založba Filozofske fakultete. Str. 359-369.
Lectures
GANTAR, Polona, 2012: Večbesedne leksikalne enote v leksikalni bazi za slovenščino : [predavanje na mednarodni konferenci Europhras 2012, Maribor, 27.-31. 7. 2012]. Maribor, 2012.
GANTAR, Polona, KREK, Simon, 2009: The “communication in Slovene” language resources project : [predavanje na mednarodni konferenci "Mondilex", Bratislava, 15.-16. 4. 2009]. Bratislava.
GANTAR, Polona, KREK, Simon, 2009: Slovene lexical database for NLP and lexicographic purposes : [predavanje na konferenci "eLexicography in the 21st century", Louvain-la-Neuve, Belgija, 22.-24. 10. 2009]. Louvain-la-Neuve.
Videolectures
KOSEM, Iztok, 2011: GDEX for Slovene. Predavanje na konferenci: Electronic lexicography in the 21st century: new applications for new users (eLex2011).
GANTAR, Polona, 2011: Kjer se srečata pomen in skladnja: Leksikalna baza za slovenščino kot vir podatkov za pedagoško korpusno slovnico. Predavanje na konferenci “Slovnica, več kot le sistem”, Ljubljana, 4. 2. 2011.
GANTAR, Polona, 2009: Leksikalna baza: vse, kar ste vedno želeli vedeti o jeziku. Predavanje na konferenci “Slovarji več kot le besede”, Ljubljana, 6. 2. 2009.
